

USING SCIENTIFIC MOULD-MAKING TECHNIQUE TO PROVIDE YOU WELL MOULD.
Part size: 20*15*5 inch
Plastic resin: PP, BPA free
Features: can be stacked
Mold material: 1.2312
Mold base: C50
Slider & lifter: H13
Injection system: Yudo hot runner
Cycle time: around 50S
As discussed with our customer, the plastic bus tubs need to be high light but with good tenacity, so we advise him to modify the PP material.
What are the methods for strengthening and heat-resistant modification of polypropylene (PP)?
Polypropylene (PP) has good heat resistance, and the products can be sterilized at a temperature above 100°C, and will not deform at 150°C without external force. However, if you want to use it at a higher temperature and will inevitably be interfered with by external forces, problems such as warpage and deformation will occur. At this time, it needs to be heat-resistant and stiffened. So, how many methods do you know about the enhanced heat-resistant modification of polypropylene (PP)?

1. PP filling modification
Filling modified PP generally refers to the addition of calcium carbonate, talc, mica powder, kaolin, wollastonite powder, barium sulfate, and other non-metallic mineral powder materials or other materials to the PP resin, which can not only significantly improve the rigidity and resistance of PP Thermal properties, improved dimensional stability, high temperature creep resistance, hardness, etc., most of them can also play an incremental role in reducing costs.
In filling modification, the first thing to do is to solve the problem of the distribution and dispersion of the filler in the PP resin matrix. At the same time, the filler needs to be properly surface treated to have a better affinity with polypropylene. It can be said that the surface treatment method of filler and the choice of surface treatment agent are the keys to the success or failure of filler modification. Nowadays, many packing manufacturers can provide different specifications and models for selection according to customer requirements. If the product quality requirements are higher, filler masterbatch can be used.
2. PP reinforced modification
Reinforcing modified PP generally refers to adding fibrous materials to PP to increase its strength, although fillers, especially fillers with large diameter-to-thickness ratios, also have the same effect. The fibrous materials used to strengthen PP mainly include glass fiber, carbon fiber, inorganic, and metal whiskers, and so on. Among them, glass fiber is the main reinforcing material, which can significantly improve the tensile strength, bending strength and modulus (rigidity), heat resistance, dimensional stability, etc. of PP plastic. Glass fiber reinforced PP can be used as engineering plastics in many occasions, such as fan blades, heater grilles, impeller pumps, lampshades, electric stoves, and heater shells, etc. As of now, the popular long glass fiber reinforced PP.
3. PP nucleation modification
Nucleation modification of PP generally refers to adding a small amount of nucleating agent to PP to significantly increase the crystallization speed, crystallization rate, and crystal fineness ratio of PP to achieve the stiffness and heat resistance modification of PP. PP nucleating agents include inorganic nucleating agents such as ultrafine talc, silicon dioxide, nano-calcium carbonate, and organic nucleating agents represented by sorbitol and its derivatives. Inorganic nucleating agents often have a certain effect on product gloss and transparency, while organic nucleating agents can significantly improve product transparency and surface gloss.
Injection mold cooling system design
1. Definition of injection mold cooling system
Injection mold cooling system: AKA. injection mold temperature control system. Heat or cool the mold to keep its temperature within a reasonable range.
* Mold cooling medium: water, oil, beryllium copper (BeCu) and air, etc.
* Mold heating methods: hot water, steam, hot oil, and heating rod, etc.

2. Influence of mold temperature on different plastics
* For plastic materials with great fluidity (PE, PP, HIPS, and ABS, etc.), lowering the mold temperature helps reduce stress cracking (the mold temperature is usually around 60°C);
* For plastic materials with poor fluidity (PC, PPO, and PSF, etc.), raising the mold temperature helps reduce the internal stress of the plastic product (the mold temperature usually ranges between 80°C and 120°C).
3. Influence of mold temperature on quality of molded plastic products
* Temperature too high: The plastic products deform greatly after mold release, and it is easy to cause flashing and sticking;
* Temperature too low: Leading to poor melt fluidity, as well as such surface defects as silver streaks, flow lines, and underfilling;
* Uneven temperature: The plastic products shrink unevenly, resulting in warping deformation.
4. Mold temperature directly affects the injection cycle
Injection mold cooling time takes up about 80% of the injection cycle.
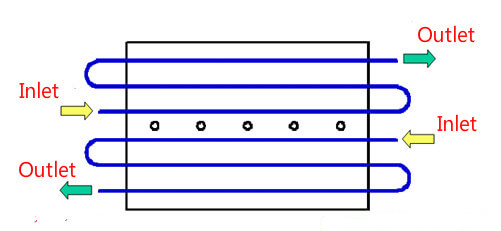
5. Ways to improve mold temperature control
* Appropriate size of cooling lines: diameter 5-13mm (3/16″-1/2″).
* Select mold materials with high thermal conductivity.
* Reasonable plastic product design.
* Proper cooling circuit.
* Enhance the cooling of the thick areas of a plastic product.
* Fast and slow cooling.
* Strictly control the temperature difference between the coolant outlet and inlet.
6. Key considerations for injection mold cooling channel design
* Which is more important, cooling or ejection?
* Try to keep the thermal balance of the mold, so that the temperature is uniform in each part of the mold.
* A parallel cooling channel is not preferred
7. Location of cooling lines
* Try to keep a consistent distance between the coolant and the filled plastic in the cavity, 10-15mm is preferred. The center distance of the coolant is about 5D.
* The cooling lines should not be close to locations where the melt flows finally meet;
* Prevent the cooling lines from interfering with other mechanisms in the mold, and maintain a steel part of 3mm in the middle;
* The coolant for the cavity insert should be as close as possible to the filled plastic, and that of the core insert should be set as far as possible to the outer edge. When the mold cavity/core is too big, the coolant must be in contact with it.
* For the BeCu mold, coolant may go straightly between plate A and plate B.

Taizhou Saiweiyue Mould & Plastic Co., Ltd.
ADD: No.12, Jinchuan Road, Beicheng Street, Huangyan District, Taizhou City, Zhejiang Province, 318020, China
Mobile/WhatsApp: +86-15757668880
Tel/Fax: +86-0576-89888400
E-mail: [email protected]
[email protected]

Copyright © Taizhou Saiweiyue Mould & Plastic Co., Ltd. Rights Reserved. OEM/ODM Injection Mold Of Plastic Restaurant Bus Tubs Suppliers